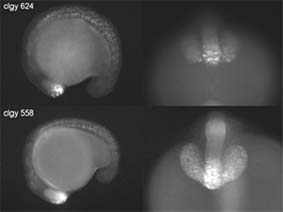
 Analysis of expression patterns is performed on a large scale by generating and imaging zebrafish transgenic for fluorescent proteins under the control of specific or endogenous enhancers (enhancer trap screening), as well as by in situ hybridization.
Analysis of expression patterns is performed on a large scale by generating and imaging zebrafish transgenic for fluorescent proteins under the control of specific or endogenous enhancers (enhancer trap screening), as well as by in situ hybridization.
More than 5,000 transgenic founder fish expressing Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) or Yellow Fluorescent Protein (YFP) under the control of zebrafish enhancer sequences are being screened, both to determine the spatial expression patterns of the corresponding genes, and to enable expression profiling in specific cell types (WP3). Most of this work is being performed at UiB, with the participation of a large number of researchers from inside and outside the consortium. UiB is also conducting research on new constructs to further enhance the efficiency of enhancer-trap screening. Moreover many project partners are generating GFP lines with specific enhancers.
The second focus is on the in situ hybridization analysis of 10,000 genes during embryogenesis. The majority of this work is being performed by CERBM. Due to the progress of the zebrafish genome project, the procedures for performing this aspect of the project have changed from using cDNA libraries as a source of genes for analysis to using gene predictions based upon Ensembl data, for which amplicons are provided to CERBM by Hubrecht Laboratory.